Passivation
Precision Cleaning For Precision Parts
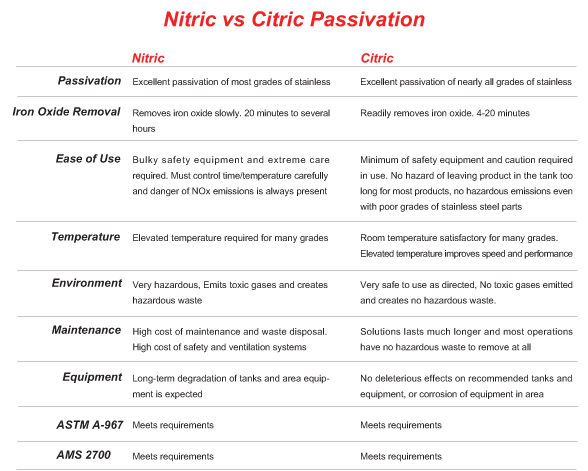
Citric Passivation
Ultrasonic cleaning with citric acid prepares the surface for WS2 and other coatings
SAE AMS 2700 E Method II
Citric Acid Passivation prevents oxidation by removing surface impurities on Stainless Titanium and Bronze. Citric Acid Passivation is a safe, clean, efficient.
For a Quick Quote
Please Call at 775-267-1244
Email us at: ericwoods@appliedtungstenite.com
Passivation
The term "passivation" means to make something chemically passive. Active surfaces react readily while passive surfaces are resistant to reactions, including corrosive reactions. "Passivating" active metals is simply to remove any iron from the surface using an acid solution.
Safe
Citric acid is safe because it does not attack the other elements in stainless steel. It removes only the iron, therefore reducing the risk to your parts. The safer chemistry allows for higher bath temperatures, which aids in bringing iron from several atom layers down to the surface at a faster rate. The safer chemistry also allows us to use ultra-sonic equipment, which enhances the cleaning powers of the acid bath.
Clean
Citric acid was specifically formulated to eliminate the safety and environmental problems of nitric acid and other mineral acids used in the passivation of stainless steel. Citric acid does not strip the nickel or chromium from the substrate therefore it does not leave heavy metals in the bath. Citric acid yields excellent results without producing hazardous waste or harmful air pollution.
Efficient
Citric acid passivation rather than nitric acid has a major advantage at the atomic level. Nitric acid attacks the surface iron first, but also diminishes the other elements in the alloy. Therefore nitric effectively limits the depth of the final passive chrome oxide layer. Citric acid, on the other hand, does not attack the other elements in stainless steel. It removes only the iron. Citric acid passivation delivers the maximum possible protective passive layer.